Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4 School of Life Science and Technology, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
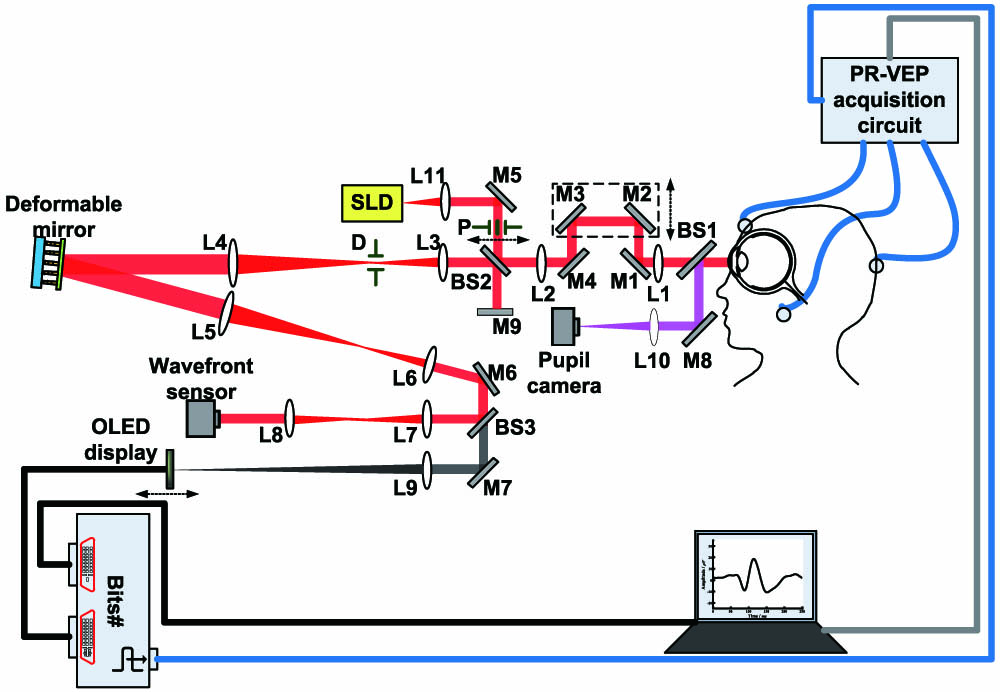
An objective visual performance evaluation with visual evoked potential (VEP) measurements was first integrated into an adaptive optics (AO) system. The optical and neural limits to vision can be bypassed through this system. Visual performance can be measured electrophysiologically with VEP, which reflects the objective function from the retina to the primary visual cortex. The VEP measurements without and with AO correction were preliminarily carried out using this system, demonstrating the great potential of this system in the objective visual performance evaluation. The new system will provide the necessary technique and equipment support for the further study of human visual function.
330.4460 Ophthalmic optics and devices 220.1080 Active or adoptive optics 330.4300 Vision system - noninvasive assessment 330.1070 Vision - acuity Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 053301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A simple and straightforward method to objectively measure the transverse chromatic aberration (TCA) at horizontal field angles out to ±10° from the visual axis of the human eye was proposed. Longitudinal chromatic aberration (LCA) was also measured across the visual field. The TCA of a human eye was obtained by deviation of the point spread function (PSF) images. LCA was calculated from the Zernike defocus. The average TCA changing with eccentricity was 0.162 arcmin/degree between 639 nm and 795 nm wavelengths. Near the optic axis of the eye, the average LCA was 0.37 ± 0.02 D, and it increased slightly with eccentricity (up to 0.54 ± 0.02 D).
330.4460 Ophthalmic optics and devices 170.4460 Ophthalmic optics and devices 330.7327 Visual optics, ophthalmic instrumentation Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(11): 113301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, P. R. China
2 The Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, P. R. China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, P. R. China
A simple method to objectively and simultaneously measure eye's longitudinal and transverse chromatic aberrations was proposed. A dual-wavelength wavefront measurement system using two Hartmann–Shack wavefront sensors was developed. The wavefronts of the red (639.1 nm) and near-infrared (786.0 nm) lights were measured simultaneously for different positions in the model eye. The chromatic wavefronts were converted into Zernike polynomials. The Zernike tilt coe±cient (first term) was used to calculate the transverse chromatic aberration along the x-direction, while the Zernike defocus coe±cient (fourth term) was used to calculate the longitudinal chromatic aberration. The measurement and simulation data were consistent.
Chromatic aberration Hartmann–Shack wavefront sensor simultaneity Zernike coe±cient Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2018, 11(4): 1850021
1 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
在早期的研究中,采用出、入瞳直径相等的双通系统进行人眼像差测量时,两个通道的奇像差相互抵消,造成奇像差(如彗差)无法测量。本文建立全新的模拟眼模型进行实验,验证双通系统在波前测量时,是否存在人眼奇像差抵消的现象。采用典型双通系统——哈特曼波前探测系统进行实验,并将出瞳光阑直径固定为6 mm,改变系统入瞳光阑大小(1~8 mm)。实验结果表明,双通系统中,人眼奇像差在出、入瞳直径相等时可测,且人眼奇像差测量与出、入瞳直径差异无关,因此人眼奇像差测量在双通系统中不存在抵消的现象。
成像系统 视觉系统 双通系统 奇像差 眼模型 抵消现象
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, P. R. China
2 The Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, P. R. China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, P. R. China
It is necessary to know the distribution of the Chinese eye's aberrations in clinical environment to guide high-resolution retinal imaging system design for large Chinese population application. We collected the monochromatic wave aberration of 332 healthy eyes and 344 diseased eyes in Chinese population across a 6.0-mm pupil. The aberration statistics of Chinese eyes including healthy eyes and diseased eyes were analyzed, and some differences of aberrations between the Chinese and European race were concluded. On this basis, the requirement for adaptive optics (AO) correction of the Chinese eye's monochromatic aberrations was analyzed. The result showed that a stroke of 20 �m and ability to correct aberrations up to the 8th Zernike order were needed for reflective wavefront correctors to achieve near diffraction-limited imaging in both groups for a reference wavelength of 550 nm and a pupil diameter of 6.0 mm. To verify the analysis mentioned above, an AO flood-illumination system was established, and high-resolution retinal imaging in vivo was achieved for Chinese eye including both healthy and diseased eyes.
Ocular aberrations adaptive optics retinal imaging Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2017, 10(1): 1650038
1 电子科技大学光电信息学院, 四川 成都 610054
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
4 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
如何有效矫正随人群起伏很大的人眼像差, 提高人眼自适应光学系统的人群适用范围是临床应用面临的最大难题。旋转双柱面镜散光补偿技术是一种使用灵活、低成本的散光补偿方法。给出了旋转双柱面镜散光矫正的理论依据, 并搭建了基于远场光斑形态的散光自动补偿实验系统, 验证了旋转双柱面镜散光矫正理论的正确性。在此基础上, 将旋转双柱面镜与人眼自适应光学系统相结合, 利用哈特曼波前测量数据调整双柱面镜, 实现了(-4~0 Dc)散光的全自动补偿, 补偿精度优于0.1 Dc, 并验证了实际人眼散光补偿效果。该技术结合Badal调焦可以为人眼自适应光学系统的大规模人群适用提供一种经济有效的低阶像差补偿方案。
视觉光学 自适应光学 旋转双柱面镜 散光 人眼像差
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
2 电子科技大学光电信息学院, 四川 成都 610054
3 成都信息工程大学控制工程学院, 四川 成都 610225
4 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 四川 成都 610209
5 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
变形反射镜作为超分辨成像系统中的光瞳滤波器,可以灵活快速地调制光场相位的性能。采用遗传算法设计具有不同超分辨参数的光瞳相位结构,通过修改自适应光学系统闭环参考矩阵实现对光瞳滤波器相位的闭环拟合。在此基础上,实验对比了不同光瞳滤波情形下的超分辨成像效果。结果表明,变形反射镜可以很好地拟合设计的光瞳滤波器相位,超分辨成像参数与理论设计值基本吻合。由于变形反射镜采用反射式并通过控制镜面面形进行超分辨光瞳相位拟合,在使用时对入射光无偏振态要求,有利于该方法的实际应用。
显微 相位调制 光瞳滤波器 超分辨 变形反射镜 激光与光电子学进展
2017, 54(4): 041801

Lina Zhao 1,2,3,4,5Yun Dai 1,4,*Junlei Zhao 1,4,5Fei Xiao 1,4[ ... ]Yudong Zhang 1,4
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The key laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Science, Chengdu 610209, China
2 University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
3 Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu 610225, China
4 Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
5 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Compared with binary diffractive super-resolving elements, programmable super-resolution pupil filters permit the analysis of various filter designs and allow the filters to be changed rapidly to modify the response of an optical system. In this Letter, a deformable mirror is employed as a programmable super-resolution pupil phase filter. Continuous phase-only filters based on the Zernike polynomial series are designed by the genetic algorithm and fitted through closed-loop adaptive optics with a piezoelectric deformable mirror. Experimental super-resolution results are in agreement with the theoretical predictions. This method has no polarization light requirement and is convenient for application.
120.5060 Phase modulation 350.4600 Optical engineering 350.5730 Resolution Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(9): 091201
1 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
由于人眼像差的多样性和不确定性,自适应光学在活体人眼视网膜高分辨率成像临床应用中受到了限制。对患有青光眼或糖尿病的中国人眼像差数据进行统计分析,并在此基础上分析了人眼像差对成像质量的影响及对波前校正器的性能需求。分析结果表明青光眼和糖尿病患者的人眼高阶像差分别是正常人眼高阶像差的2.9和1.8倍,为了获得接近衍射极限分辨率的视网膜图像,对这两类病眼的像差校正均应该高于8阶泽尼克多项式,并且波前校正器的行程需要分别达到39 μm和14 μm以上。分析结果对基于自适应光学的临床眼科仪器开发有一定的指导意义。
自适应光学 人眼像差 波前校正 视网膜成像 光学学报
2015, 35(s1): s133001
1 中国科学院光电技术研究所自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
结合人眼自适应光学系统中无需复原Zernike模式系数的特性,提出基于控制信号重置的双变形镜并行控制的改进算法,改进后的算法可以减少矩阵运算量,并能相应地减少存储空间,使其适宜于人眼自适应光学系统的工作特性。对控制算法进行理论介绍,通过模拟仿真证明其可行性,并将算法应用于双变形镜人眼视网膜高分辨率成像系统,实现了对双变形镜的快速稳定控制,获得了眼底视网膜高分辨率图像。模拟仿真和实验结果表明,该算法能够有效地补偿相伴畸变和抑制两个变形镜之间的耦合。
自适应光学 双变形镜 并行控制 视网膜成像 光学学报
2015, 35(s1): s101007





